A step-by-step guide - mechanical damage tool
General
Select Modules from the start-up page and then select Incorrect relative humidity as an agent of deterioration. A list of deterioration processes for which risk may be quantitatively assessed by means of available tools is displayed. Select the Mechanical damage tool.
Alternatively, select Tools in the upper menu line and select the Mechanical damage tool from the list.
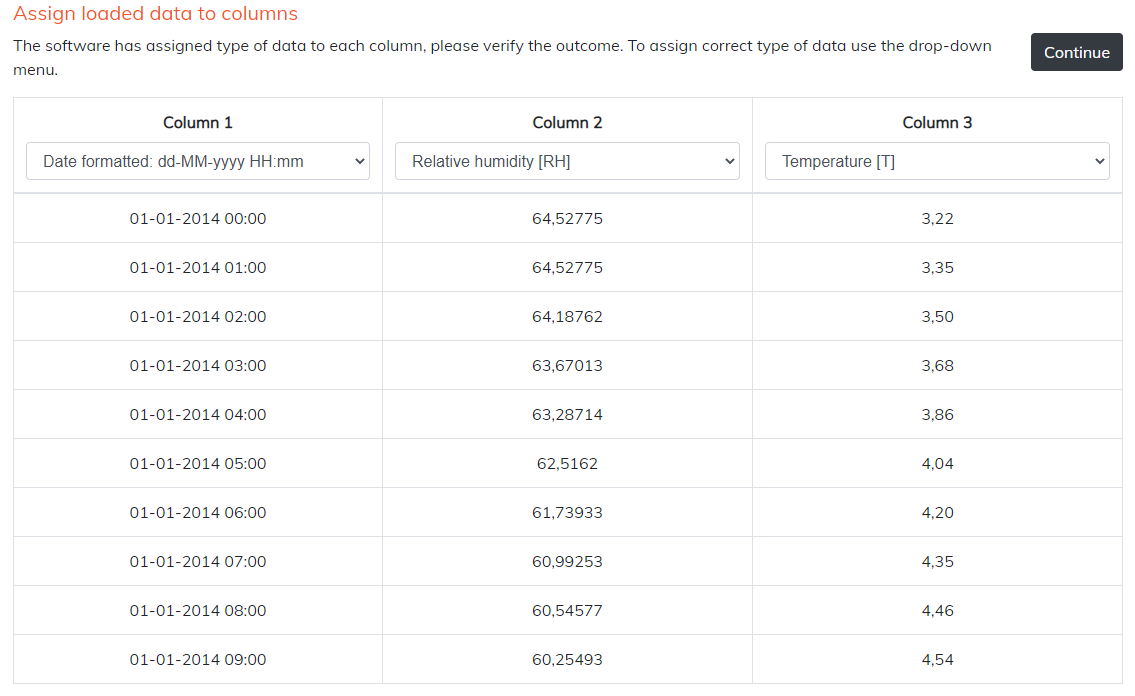
The list of data sets available for calculations is displayed with the average levels of relative humidity and temperature over the period covered by the data. You can view plots of each data set by selecting Graph. From the list, select one or more data sets to perform calculations. Press Proceed to calculations which takes you to the Your calculations page.
Select the data sets for which you would like to perform calculations of the strain versus time history for a given object. After pressing the New calculation button, choose the object of interest: a freely responding wooden panel covered with a gesso layer (painting on wood), a restrained wooden panel (restrained wood) or a sheet of parchment (parchment). Press Proceed to advance to the list of variables that must be specified to perform the calculations (clicking on question marks explains the details of the available options).
Wooden panels
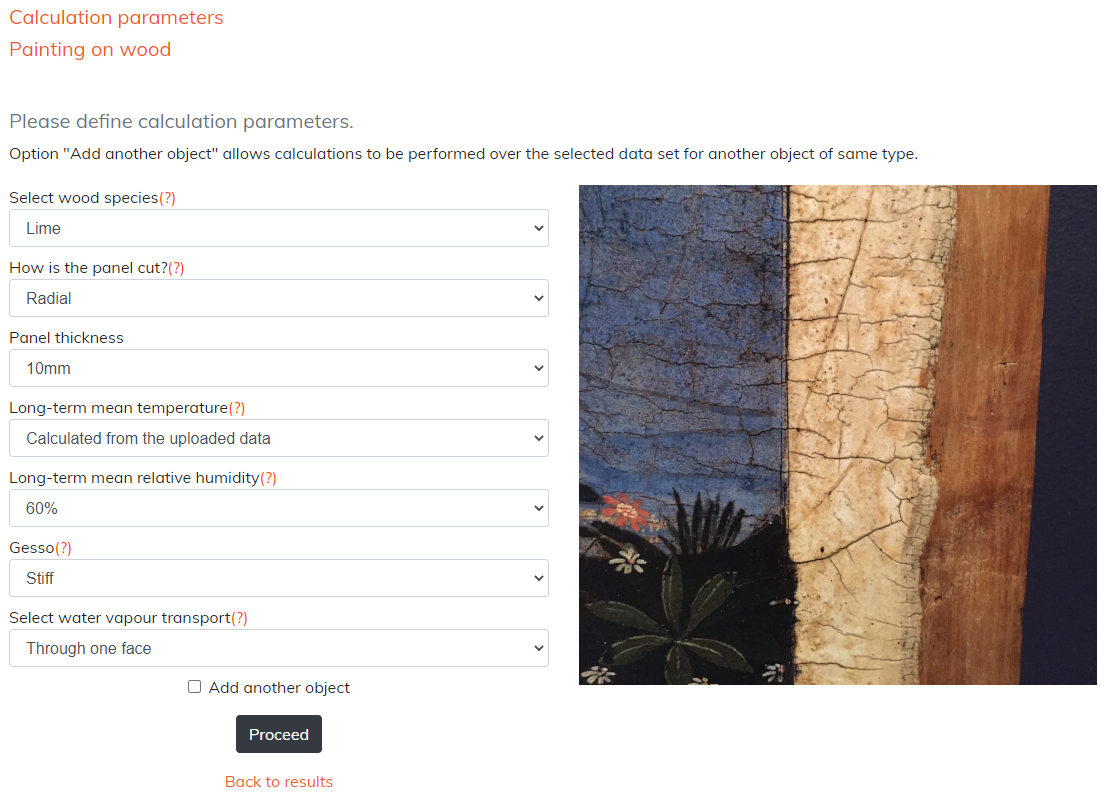
First, the wood species and cutting orientation need to be selected, followed by the panel thickness. Next, the long-term mean temperature and relative humidity for which the user wants to obtain the results can either be calculated from the uploaded data, or entered from the provided list. By selecting the long-term mean climate parameters calculated from the uploaded data, you assume that your object has acclimatized to the climate represented by these data. By selecting the long-term mean parameters yourself, you assume that your object has acclimatized to past climate conditions represented by these selections, and you seek information on the object response to the transition from this past environment to the conditions recorded. If a freely responding gesso covered panel is selected, the stiffness of the gesso also needs to be specified. Finally, the type of water vapour transport through the object must be defined.
Specifications for freely responding panel painting on lime wood, radially cut, 10 mm thick, for a mean temperature calculated from the data (HERIe – example 1) and a mean relative humidity of 60%, with stiff gesso and one face open to water vapour transport, are shown below as an example.
Parchment
As parchment is a material with fast moisture response, only the long-term mean relative humidity, for which the user wants the obtain results, needs to be either calculated from the uploaded data or chosen from the provided set.
Calculation
Check Add another object, click Proceed and specify variables for the second object of the same type considered. Continue in the same way until variables for all objects of interest are specified. Then click Proceed to calculate the strain versus time histories induced by the data set selected for all objects specified. The software takes you back to the Your calculations page in which the list of calculation results is displayed with the average levels of relative humidity and temperature over the period covered by the data. Select one or more results to view the plots, download or remove the data.
Important remark: You always need to select the data sets of interest during each HERIe session, even if you want to simply view the results of the calculations already performed.